NVIDIA Launches NVLink Fusion Program to Expand Data Center Market Influence
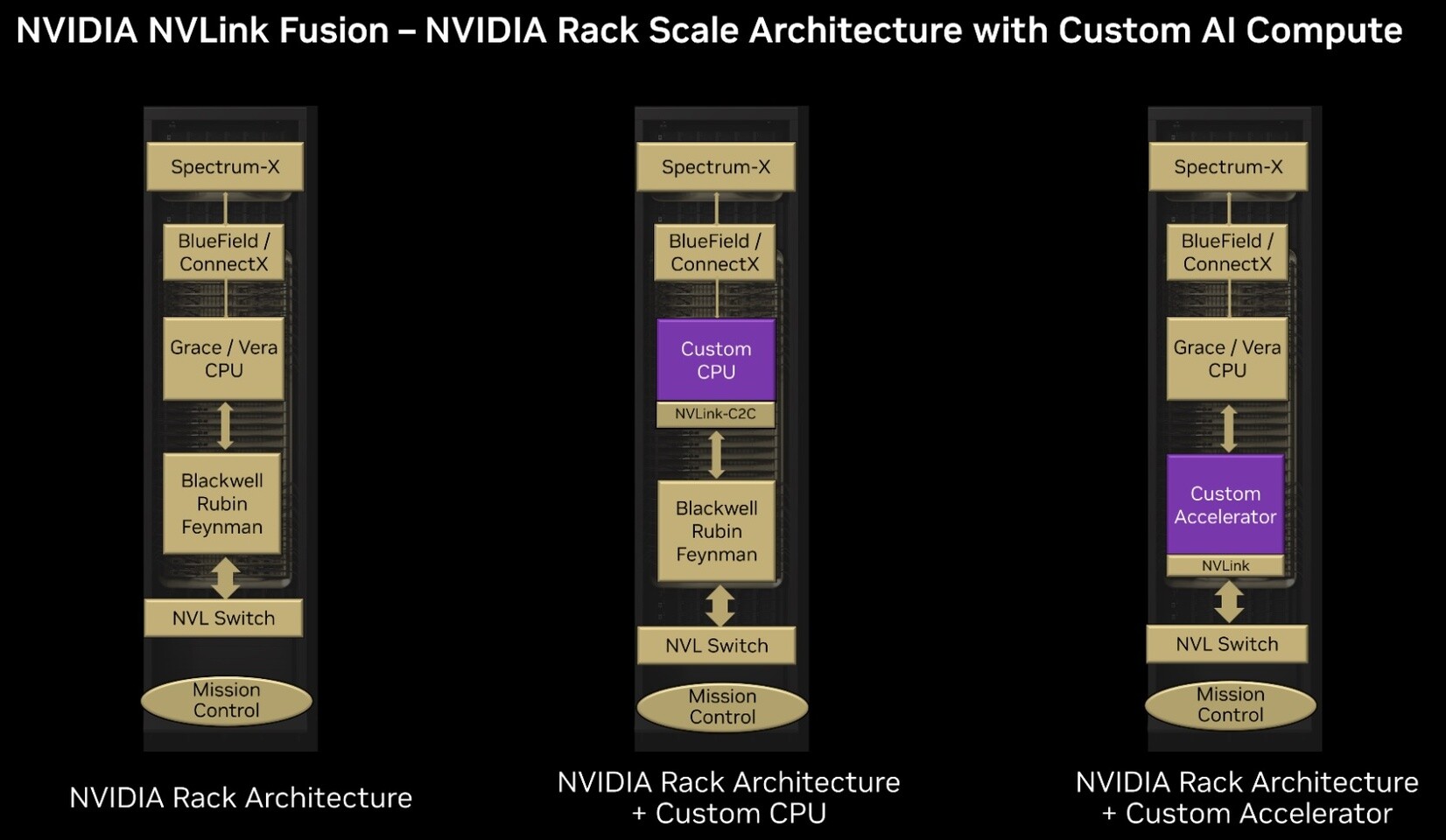
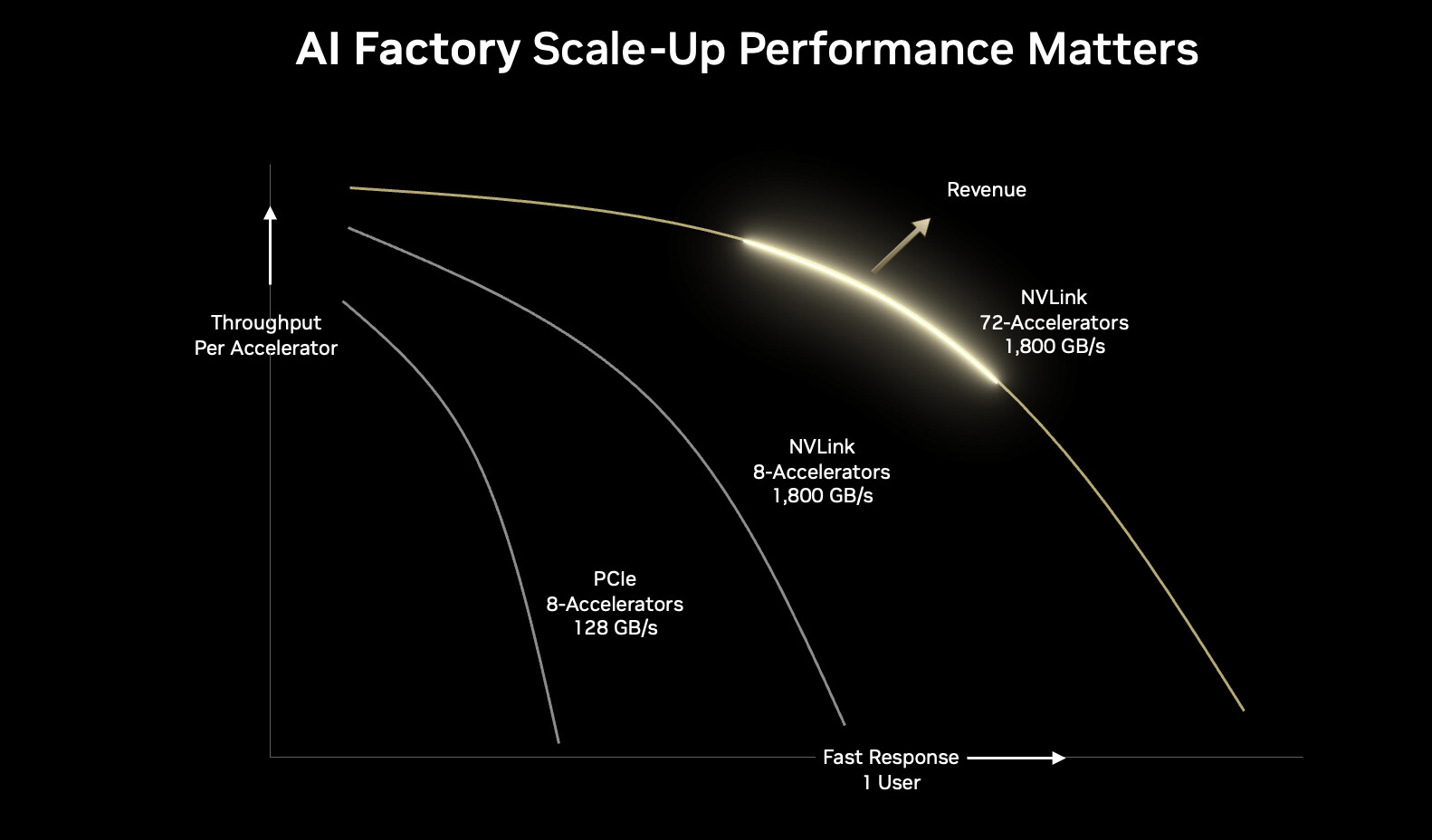
In order to increase its presence in the data center market, NVIDIA has recently introduced the NVLink Fusion program. This initiative allows selected partners to incorporate their custom-designed chips into the NVIDIA system framework. For instance, a partner can link its custom CPU to an NVIDIA GPU using the 900 GB/s NVLink-C2C interface. However, there are certain restrictions associated with this collaboration. Any custom chip must be connected to an NVIDIA product, and the company maintains strict control over the crucial software that oversees these connections. This implies that partners are unable to create fully independent, mix-and-match systems. NVIDIA retains authority over the essential communication controller and PHY layers in the NVLink Fusion, which establish and manage these connections. It also requires a license for third-party hardware to utilize its NVLink Switch chips.
In response, a coalition of major tech companies, including AMD, Google, and Intel, is advocating for an open-standard alternative. The UALink Consortium unveiled its 1.0 specification in April 2025, outlining a public standard for linking up to 1,024 accelerators from any vendor. While NVIDIA currently offers higher raw bandwidth, UALink signifies a shift towards increased flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Reports indicate that eight companies have shown interest in NVLink Fusion. However, the frustration of dealing with a communication link that lacks transparency leads to designs that may not always be optimal and efficient. NVIDIA establishes these guidelines upfront, so any company willing to collaborate with NVLink Fusion is informed of these limitations from the start. Cloud hyperscalers like AWS, GCP, and Azure are among the reported eight customers who have shown interest, indicating that they may accept these conditions and continue working with NVIDIA to access the IP despite the limited information available.